Nexus
From scheduling appointments to retrieving information, personal assistants have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. In a world where the volume and complexity of digital tasks continue to expand, having an intelligent companion to handle these tasks efficiently becomes ever more crucial. While giants like Google, Amazon, and Apple have made strides in this direction, I recognized the need for a solution that transcends brand boundaries and empowers users to harness the full potential of a personal assistant.
This project has a pretty big scope and for this reason i’m slowly chipping away at it every now and then, slowly building it’s capabilities and functionality, it’s still a work in progess and probably will for some more time.
The Challenge: Closed Systems and Privacy Concerns
From scheduling appointments to retrieving information, personal assistants have the potential to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. In a world where the volume and complexity of digital tasks continue to expand, having an intelligent companion to handle these tasks efficiently becomes ever more crucial. While giants like Google, Amazon, and Apple have made strides in this direction, I recognized the need for a solution that transcends brand boundaries and empowers users to harness the full potential of a personal assistant.
This project has a pretty big scope, and for this reason I’m slowly chipping away at it now and then, slowly building its capabilities and functionality. It’s still a work in progress and probably will be for some time.
The Challenge: Closed Systems and Privacy Concerns
Traditional personal assistants, while promising, often come shackled within proprietary ecosystems. This closed approach not only limits their utility but also raises concerns about data privacy. With the desire to create a more flexible and secure alternative, I set out to build Nexus—an open-source infrastructure that enables anyone to run their own personal assistant on a private server. This infrastructure empowers users to customize their assistant’s capabilities and expand its skill set, all while retaining control over their data.
A Peek into Nexus: How It Works
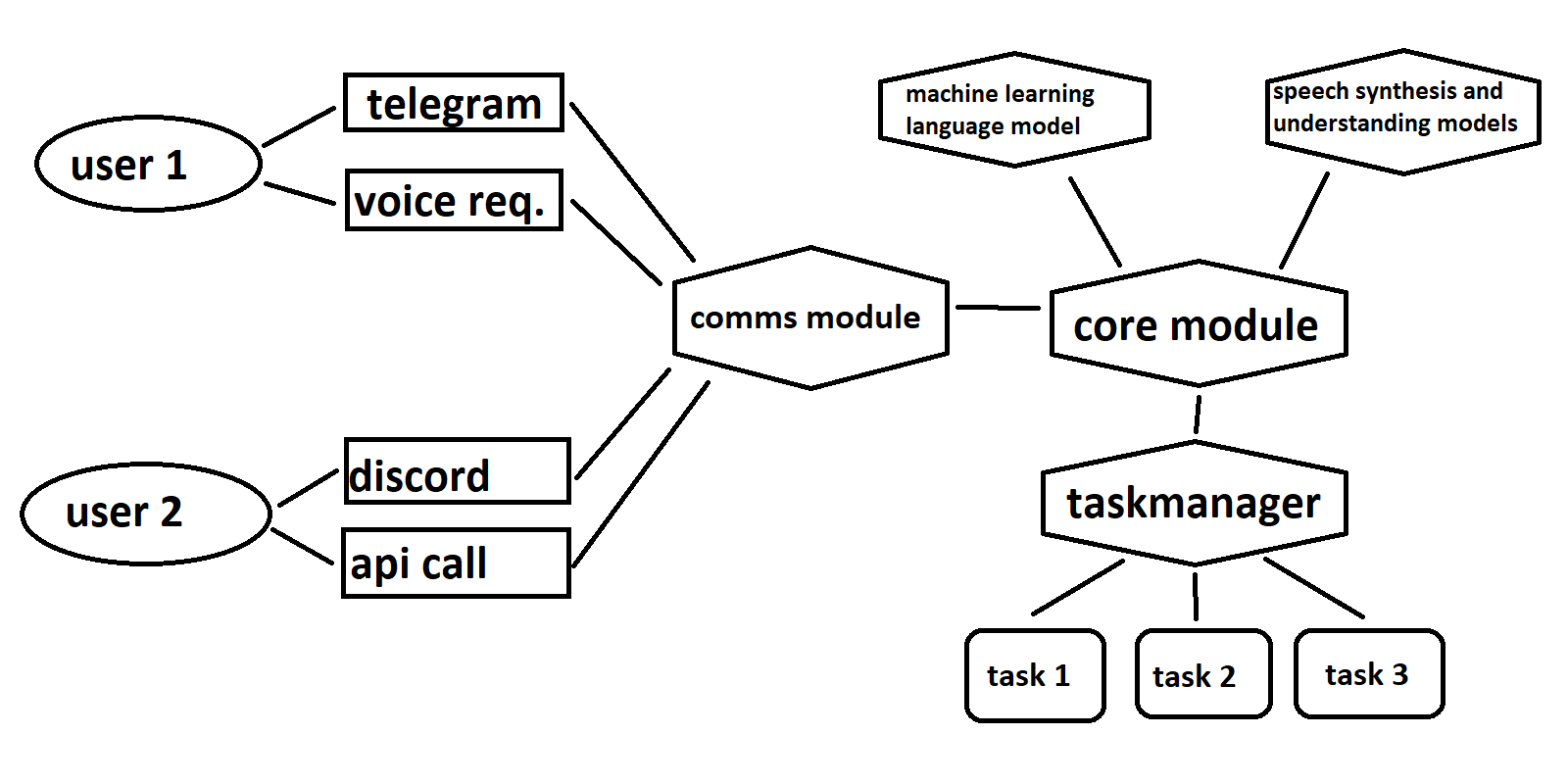
Nexus is more than just a personal assistant; it’s a comprehensive cluster of services designed to collaboratively execute tasks on behalf of the user. Each service operates independently, communicating via API calls to ensure a modular and adaptable architecture. This modularity allows each service to be tailored to specific needs, enabling diverse functions like high-level logic processing in Python or compute-intensive tasks handled by modules written in languages like C++ or Rust.
At its core, Nexus operates through a sophisticated orchestration process. When a user submits a task request, the system’s core module springs into action. It interprets the user’s intent using advanced natural language processing techniques—an approach known as “intent classification.” This process analyzes the user’s input, be it a typed message or a transcribed speech, and calculates the likelihood of that input belonging to predefined categories. This powerful technique ensures accurate task understanding.
Once the task is comprehended, the core module gathers any missing contextual information required for task execution. For instance, if the task involves providing the weather forecast for the next two hours, but the location is missing, Nexus intelligently prompts the user for this information. The gathered data is then passed to the task manager, who is responsible for spawning independent processes to perform the requested tasks.
The task manager forms the heart of Nexus’s functionality. It houses the intricate logic necessary to execute a task seamlessly. Importantly, this is also where users can contribute to the system’s growth. To teach Nexus a new task, users need only write the task’s logic, accompanied by a bit of standardized code. The modular nature of the system ensures that this new capability integrates seamlessly into the assistant’s skill set, ready to be deployed the next time it’s needed.
You can find the source code over at GitHub
 ElPlatypo
ElPlatypo